
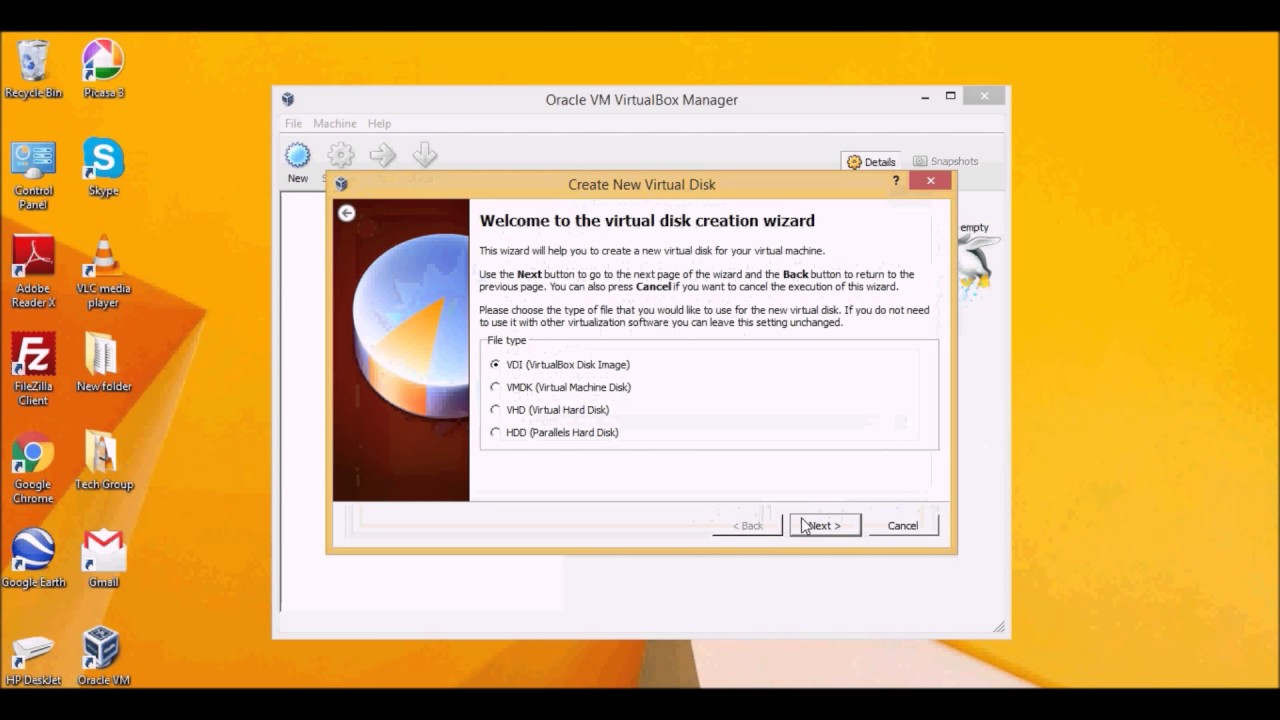
You’ll see the default VDI storage location and size on the next screen, leave them as they are, and select Create.Choose Dynamically allocated and select Next.Choose VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image) and select Next. Next, you’ll need to choose the type of file you’d like to use for the virtual hard disk.Select your host according to your operating system. Choose the Create a virtual hard disk now option and click Create. Step 1: Downloading Virtual Box Download Virtual box from here. Right-click on the installer and select ' Run as Administrator '. not on 'Desktop', or 'Documents', but to 'Public/Downloads' for example. A guest OS is an operating system installed on a virtual machine running inside VirtualBox. Download (if you havent already) the latest VirtualBox and its matching ExtPack (5.1.10 as of this writing). VirtualBox can be installed on Windows, Linux, macOS, Solaris, and FreeBSD. On VirtualBox you can run VMs with Windows, Linux, macOS, Solaris, FreeBSD, Novell Netware, and other operating systems. On the next screen, you’ll need to create a new hard disk for your virtual machine. Let’s explore how to set up VirtualBox on Windows.You have two options to choose from you could either use Dynamically allocated storage which grows as you keep using the storage, or allocate a Fixed-size storage limit that offers faster performance. Step 1: Open Oracle VM VirtualBox Step 2: Create Virtual Machine Step 3: Attach Ubuntu 22. This portion will only be accessible to your virtual operating system, i.e., Ubuntu in this case. You’ll also need to allocate a portion of your hard disk to the virtual machine. For instance, if you have 16GB total RAM, allocate 4GB to the virtual machine. Ideally, you should choose to allocate about a fourth of your PC’s RAM. Allocate Memory size to your virtual machine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
